In light of international nurses day; we thought we would pay tribute to all our wonderful nurses by giving you a brief insight into the history of the nursing profession
taking you back to where it all began.
The word “nurse” originally came from the Latin word “nutrire”, meaning to suckle, referring to a wet-nurse; only in the late 16th century did it attain its modern meaning of a person who cares for the sick.
Since the earliest times, most cultures produced a stream of nurses dedicated to service on religious principles. Only in the 20th century did nursing become a secular profession advanced mainly through the rise of warfare.
India shows the earliest recorded history of nursing practice. The earliest Indian medicine was Ayur Veda Medicine found in Veda 5000 B.C. About 1400 B.C. Charaka,the father of medicine,wrote a book on internal medicine. Doctors and attendants or nurses had to be people of high moral character. Bhuddhist King Ashoka B.C.226-250,ordered the building of monasteries and hospitals for men and animals along the routes of travellers so that the sick would be treated at the expense of the state. Hygienic practise was adapted and first importance was given to prevention of diseases. Nurses were usually men or old women.
Travelling further east to China, advances in medicine were much in the lead .Before 2000 B.C, medical professionals were allowed to practice dissection. They knew about circulation of blood and had good description of the internal organs. Their slogan was Look, Listen, Ask and Feel. By 100B.C. vaccinations were being used and diseases such as syphilis and gonorrhoea were recognised as well as the use of liver diets for anaemia, seaweed or iodine for thyroid conditions and chaulmoogra oil for leprosy by 3000 A.D. However, nursing was not practised as they believed that disease was due to evil spirits in the patient and they might enter anyone who touched the sick person.
Later in history, Greek physician; Hippocrates gave scientific views to medicine. He taught doctors about signs and symptoms of diseases. The treatment was based on diagnosis. He developed ways of doing physical examination and taking histories.He gave instructions in hot applications, poultices, cold sponge for fever, fluid for kidney diseases and mouth washes. Rome learnt a lot from Greece about medicine and much like in India, nursing was practiced by old women and men of good character.
When Muhammad founded Islam in the early 7th century, faithful Muslims became nurses to manifest their love of Allah. Arab ideas were later influential in Europe. The famous Knights Hospitaller arose as a group of individuals associated with an Amalfitan hospital in Jerusalem, which was built to provide care for poor, sick or injured Christian pilgrims to the Holy Land.
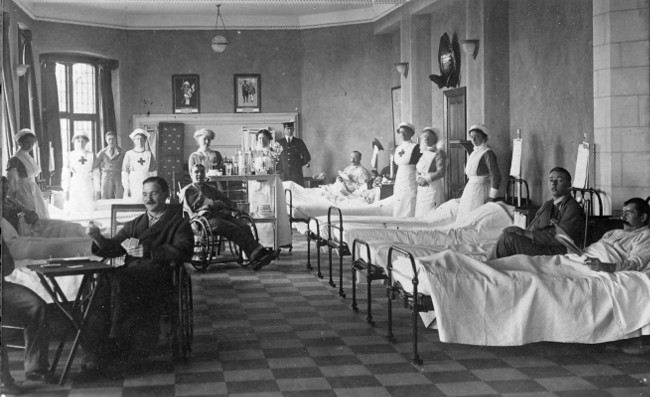
Around the early to late 1900’s, nursing was becoming more important than ever, as nurses were needed on the front lines of the many wars being waged, from the Crimean War to the Civil War. Nurses were sent to attend to the sick and wounded soldiers in battle, shaping the practice of nursing for what we know it to be today. English nurse, Florence Nightingale began her nursing career as a nurse within the Crimean War that took place in the mid 1850’s, tending to injured soldiers on the battlefield. During this time, deaths from injuries were commonplace, due to the lack of general hygiene and the huge amount of fatal infections that resulted from these wounds.
Upon encountering this, Nightingale asked for and received aid from the British government that allowed for much better hygiene throughout the battlefield and nearby hospital. It was due to this that the rate of death from infections dropped drastically in but a short period of time. Throughout the rest of her life, Nightingale advocated for sanitary living conditions for patients, as well as providing similar designs to be implemented within hospitals, an ideal that has spread throughout the entirety of the nursing profession throughout the following years.
In 1866, nurses were formally appointed to Military General Hospitals. These military nurses were sent overseas beginning with the First Boer War (often called Zulu War) from 1879 to 1881. They were also dispatched to serve during the Egyptian Campaign in 1882 and the Sudan War of 1883. Almost 2000 nurses served during the second Boer War.
New Zealand was the first country to regulate nurses nationally, with adoption of the Nurses Registration Act on the 12 September 1901. It was here in New Zealand that Ellen Dougherty became the first registered nurse.
Today we know nurses to be those at the forefront of medicine with the ability to lift patients twice their size, bladders of steel to survive beyond-busy shifts, laser-beam focus to juggle multiple patients, lightning-quick response to emergencies and unexpected contingencies and future vision to foresee patients’ needs. Nurses are the caring people who give you all the detailed information that doctors often oversee regarding side- effects, general health and psychological well being. Nurses act as the mediator between the patient and their doctor offering support and a caring hand. They are on the front-lines of patient care being exposed to infectious conditions, needles, chemicals and bodily fluids. What you see on TV is not the reality of nursing! Nurses don’t have their hair and make-up professionally done before work each day/night, patients always come first; even when our nurses haven’t eaten in hours or had a bathroom break all day- your needs will precede their own. Nurses will stand up for you, they are afraid when something goes wrong, they think about you off the clock and they are there when you need someone the most. Thank you to all our dedicated nurses for your hard work and giving hearts!